Distributed Feedback Laser
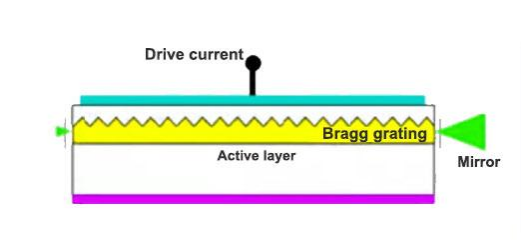
Distributed feedback laser (DFB) is a type of laser device that utilizes a diffraction grating to create an active region in a device, enabling it to emit light with a narrow line width. DFB lasers have become increasingly popular in industries and research laboratories due to their wide range of applications, such as optical communications, sensing, and medical technology.
Compared to other types of lasers, such as quantum-cascade or optical-fiber lasers, DFB lasers have unique advantages. For example, they offer stable output over time and temperature, low power consumption, and greater tolerance for misalignment in the optical system. Additionally, DFB lasers can produce light with reduced spectral line widths compared to alternative laser sources.
https://www.instagram.com/lasersonly
https://www.instagram.com/fiberopticsclub/?hl=en
The main applications for DFB lasers:
Distributed feedback laser devices use a diffraction grating for their active region, making them ideal for different scientific and industrial tasks. Their unique properties and design features enhance accuracy and performance compared to standard laser technologies.
One primary application of DFB lasers is in optical communications, which can be used in high-speed systems such as fiber-optic cables. The narrow spectral line widths enabled by the diffraction grating allow greater flexibility, allowing multiple signals to be coded onto one carrier or wavelength. As a result, these DFB fiber laser systems are increasingly reliable and robust, with less power consumption than traditional lasers.
DFB laser diodes can also be found at the heart of sensing systems, such as those used in astronomy, optical imaging, or chemical detection. The ability to produce light with high-resolution line widths enables accurate monitoring and tracking of various aspects of the environment around us, increasing safety and efficiency in many sectors.
The most significant advantages of DFB laser diode systems include the following:
- They have excellent stability over time and temperature when operated at higher power levels due to their reduced sensitivity to thermal stresses.
- Lower power consumption requirements.
- Improved tolerance for misalignment within optical systems.
- Enable higher speed in optical communications through narrow spectral linewidths that allow multiple signals to be coded onto one carrier or wavelength.
- They can produce light with high resolution, making them ideal for use in sensing systems such as those used in astronomy, optical imaging, or chemical detection.
- Complex active components and periodic structures enable better performance than alternative laser technologies.
Top Manufacturers of DFB lasers:
Eblana Photonics LTD: Dublin, Ireland. They specialize in MIR and NIR laser diodes. They have been in business since 2001 and have years of experience with DFB laser diodes.
CSRAyzer Optical Technology: Wuhan, China, They are an optical device supplier to a worldwide audience. They have been in business since 2013 and have one of the world’s most extensive production facilities for DFB lasers.
Frankfurt Laser Company: Friedrichsdorf, Germany. The team here has experience with DFB DBR and FP laser diodes. They offer a massive selection of power ranges and have been in business since 1994.
Conclusions:
Overall, distributed feedback laser diodes are powerful tools for scientists in many fields due to their unique properties, enabling better accuracy and performance than some standard laser technologies. As research continues into developing DFB devices, further advancements will likely lead to even broader capabilities for this type of laser diode.